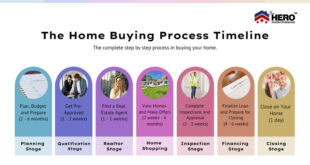
Loan-to-Value Ratio Explained: Optimize Your Finances. The Loan-to-Value (LTV) ratio is a crucial metric in the financial world, especially when it comes to securing loans or mortgages. Understanding the LTV ratio can help borrowers make informed decisions and improve their chances of loan approval. In this article, we’ll break down the concept of the Loan-to-Value ratio, its significance, how to calculate it, and tips to optimize it for your financial goals.
What is the Loan-to-Value (LTV) Ratio?
The Loan-to-Value ratio is a financial term used by lenders to assess the risk of lending to a borrower. It represents the percentage of a loan amount compared to the appraised value of the asset being purchased. A lower LTV ratio indicates lower risk for the lender, while a higher LTV ratio implies higher risk.
For example, if you’re buying a home worth $200,000 and you’re borrowing $150,000, the LTV ratio would be 75%.
Why is the Loan-to-Value Ratio Important?
- Risk Assessment for Lenders: Lenders use the LTV ratio to evaluate the risk associated with lending. A lower LTV ratio means the borrower has more equity in the asset, reducing the lender’s risk.
- Impact on Loan Approval: Many lenders have maximum LTV thresholds. Exceeding these limits could result in loan denial or higher interest rates.
- Influence on Loan Terms: LTV ratios can affect your loan’s interest rate, down payment requirements, and mortgage insurance.
- Determines Equity: The LTV ratio shows how much equity you have in an asset. Higher equity means better financial stability and borrowing power.
How to Calculate the Loan-to-Value Ratio
The formula for calculating LTV ratio is simple:
LTV Ratio (%) = (Loan Amount / Appraised Value) × 100
Example Calculation:
- Loan Amount: $150,000
- Appraised Property Value: $200,000
LTV Ratio = ($150,000 / $200,000) × 100 = 75%
Optimal Loan-to-Value Ratios for Different Loans
1. Mortgages:
- Conventional loans typically require an LTV ratio of 80% or less to avoid private mortgage insurance (PMI).
- FHA loans may allow LTV ratios as high as 96.5%, requiring a smaller down payment.
2. Auto Loans:
- Lenders prefer LTV ratios below 100%. An LTV above 100% means you’re borrowing more than the vehicle’s value.
3. Home Equity Loans:
- Most lenders cap the combined LTV ratio (existing mortgage + home equity loan) at 85%.
Factors Affecting the Loan-to-Value Ratio
- Down Payment: A larger down payment reduces the loan amount, lowering the LTV ratio.
- Appraised Value: A higher appraised value reduces the LTV ratio if the loan amount remains unchanged.
- Loan Amount: Borrowing less than the asset’s value lowers the LTV ratio.
- Market Conditions: Changes in property values can impact the LTV ratio over time.
Benefits of a Low Loan-to-Value Ratio
- Better Loan Terms: Lower interest rates and more favorable repayment terms.
- Reduced Costs: Avoidance of private mortgage insurance and other fees.
- Increased Approval Odds: Lenders are more likely to approve loans with low LTV ratios.
- Greater Financial Security: More equity in the asset offers financial stability.
Drawbacks of a High Loan-to-Value Ratio
- Higher Costs: Increased interest rates and the potential requirement for PMI.
- Risk of Negative Equity: Market value declines could result in owing more than the asset’s worth.
- Loan Denial Risk: Exceeding LTV thresholds could result in rejection of loan applications.
Tips to Improve Your Loan-to-Value Ratio
- Increase Your Down Payment: Save more before applying for a loan to reduce the amount borrowed.
- Choose Affordable Properties: Opt for assets within your budget to lower the LTV ratio.
- Negotiate the Appraised Value: Ensure the property appraisal reflects its true market value.
- Refinance Strategically: Consider refinancing when property values increase to reduce your LTV ratio.
- Pay Down Existing Loans: Make extra payments to lower the loan balance and improve your LTV ratio.
10 Tips for Managing Your LTV Ratio
- Save at least 20% of the property’s value for a down payment.
- Compare lenders for the best LTV thresholds.
- Regularly monitor property value trends.
- Refinance loans when property values rise.
- Avoid over-borrowing beyond the asset’s worth.
- Use windfalls to make lump-sum loan payments.
- Consider government-backed loans for higher LTV allowances.
- Maintain a good credit score for better loan terms.
- Choose assets with stable or appreciating values.
- Plan your finances to avoid relying on high LTV loans.
10 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Loan-to-Value Ratio
1. What is a good Loan-to-Value ratio? A good LTV ratio is 80% or lower, as it reduces lender risk and costs for the borrower.
2. Can I get a loan with a high LTV ratio? Yes, but it may come with higher interest rates and additional requirements like PMI.
3. How does the LTV ratio affect my mortgage? It impacts loan approval, interest rates, and the requirement for mortgage insurance.
4. What’s the difference between LTV and CLTV? CLTV (Combined Loan-to-Value) includes all loans on the property, while LTV considers only the primary loan.
5. Can I reduce my LTV ratio over time? Yes, by making extra payments or benefiting from property appreciation.
6. What happens if my LTV ratio exceeds 100%? You’d owe more than the asset’s value, risking negative equity.
7. Does LTV ratio affect auto loans? Yes, lenders consider it to ensure the loan amount doesn’t exceed the vehicle’s value.
8. Is LTV ratio the same for all types of loans? No, it varies depending on the loan type and lender’s criteria.
9. How can property appraisal errors affect my LTV ratio? An inaccurate appraisal can distort the LTV ratio, affecting loan terms or approval.
10. Can a cosigner improve my LTV ratio? No, a cosigner doesn’t affect the LTV ratio directly but can improve approval chances.
Conclusion
The Loan-to-Value ratio is a vital metric in the lending process, influencing loan approval, terms, and costs. By understanding and managing your LTV ratio, you can secure better financial deals and achieve long-term financial stability. Whether you’re applying for a mortgage, auto loan, or home equity loan, optimizing your LTV ratio is key to financial success.
By following the tips and insights shared in this guide, you’ll be better equipped to navigate the complexities of the LTV ratio and make informed decisions for your financial future.
 mortgage.kbk.news
mortgage.kbk.news